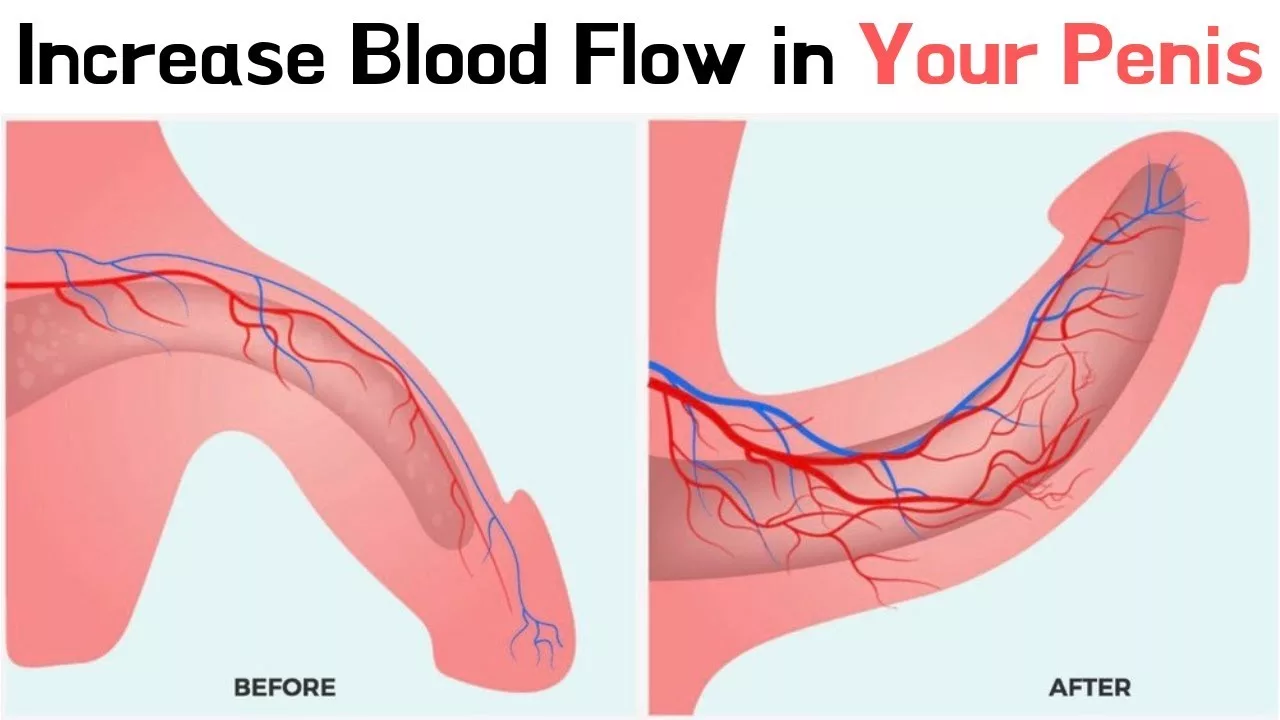
What Causes Erectile Dysfunction (ED) in Men?
ED in Men | Can Masturbation Cause ED? | Shockwave Therapy for ED
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a widespread condition that can have a significant impact on a man’s quality of life and self-esteem. It is defined as the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfying sexual performance. While ED is common, it is far from simple, and its causes can be complex and multifaceted. In this extensive blog post, we will explore in-depth the causes for erectile dysfunction along with diverse factors that contribute to the development of ED, including physical, psychological, and lifestyle-related causes.
What is Erectile Dysfunction (ED)?

Erectile Dysfunction, often referred to as impotence, is the inability to achieve or sustain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. It is essential to distinguish between occasional difficulty achieving an erection and persistent erectile dysfunction. Occasional difficulties can happen to most men and are not necessarily a cause for concern. However, when ED becomes a recurring issue, it may be classified as a medical condition.
How Common is Erectile Dysfunction?

For men, erectile dysfunction (ED) can be a nightmare. Despite being a natural and often reversible condition, many men feel too embarrassed to seek treatment. If you’re experiencing ED, you might feel ashamed to talk about it. However, both you and your partner(s) will feel much better when you understand the causes and treatments.
These data points won’t go soft on you:
- One-third of all men are affected by erectile dysfunction, and the prevalence increases with age.
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED) affects as many as 30 million American men.
- Of all continents, Europe has the highest rate of erectile dysfunction, and South America has the lowest.
- Men with diabetes are 2-3 times more likely to develop ED.
- Vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and high cholesterol account for 70% of physical-related causes of ED.
- Depressed men are twice as likely to have ED, and many treatments for major depressive disorders can cause ED.
- One survey found that 39% of men with ED never sought treatment for it.
- 36% of men in one survey reported experiencing no side effects from their ED medication.
I. Physical Causes of Erectile Dysfunction

Erectile dysfunction (ED), often referred to as impotence, is a condition where a man consistently struggles to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. Physical causes of ED are related to problems with the body’s physical structures or processes that affect the ability to achieve and sustain an erection.
Here are some of the primary physical causes of erectile dysfunction:
A. Vascular Issues
One of the primary physical causes of ED is related to blood flow. Conditions such as atherosclerosis, where arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the accumulation of plaque, can restrict blood flow to the penis. This diminished blood flow prevents the penis from becoming sufficiently engorged to achieve and maintain an erection.
B. Neurological Conditions
Diseases like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries can interfere with the transmission of nerve signals to the penis, impairing the ability to achieve and maintain an erection. Nerve damage can disrupt the complex series of events required for an erection to occur.
C. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal changes, particularly a decrease in testosterone levels, can contribute to ED. This hormonal shift is more common in older men but can affect men of all ages. Testosterone plays a crucial role in maintaining sexual desire and function.
D. Medications and Side Effects
Certain medications, such as those for hypertension, depression, and prostate cancer, can have ED as a side effect. It’s crucial to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider and explore alternative treatments if necessary.
E. Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can cause damage to blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of ED. Proper management of blood sugar levels is essential in mitigating this aspect.
F. Peyronie’s Disease
Peyronie’s disease is a condition characterized by the development of fibrous scar tissue inside the penis, leading to curvature and pain during erections. It can also contribute to ED by affecting the structural integrity of the penis.
G. Sleep Disorders and ED
Sleep disorders like sleep apnea can disrupt oxygen supply during sleep, leading to reduced testosterone levels and ED. Addressing sleep issues can have a positive impact on sexual health.
H. Prostate Issues
Prostate problems, including prostate cancer and its treatments, can damage nerves and blood vessels crucial for erections. Men who undergo prostate surgery or radiation therapy are at an increased risk of developing ED.
II. Psychological Causes of Erectile Dysfunction

While physical factors like vascular issues or hormonal imbalances can contribute to ED, psychological factors can also play a significant role. Psychological causes of erectile dysfunction are related to emotional, mental, or relational issues that interfere with sexual function.
Here are some common psychological causes of ED:
A. Stress and Anxiety
Psychological factors, including stress and anxiety, are among the most common causes of ED. Stress-related hormones can constrict blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the penis and impeding the ability to achieve an erection.
B. Depression
Depression can affect both the desire for sex and the ability to achieve an erection. It may also lead to reduced energy levels and motivation, which can contribute to ED.
C. Relationship Issues
Problems in a relationship, such as communication issues, trust problems, or unresolved conflicts, can have a significant impact on sexual performance and may lead to ED. Emotional intimacy and a sense of security in a relationship are closely linked to sexual satisfaction.
D. Performance Anxiety
Performance anxiety, often triggered by the fear of not being able to perform adequately in bed, can become a self-fulfilling prophecy. Men may become so preoccupied with their performance that they are unable to relax and enjoy the sexual experience, leading to ED.
E. Past Trauma and Emotional Scars
Past traumatic experiences, including sexual abuse or assault, can create emotional scars that affect a person’s ability to engage in intimate and sexual relationships. These emotional wounds can manifest as ED in adulthood.
III. Lifestyle-Related Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
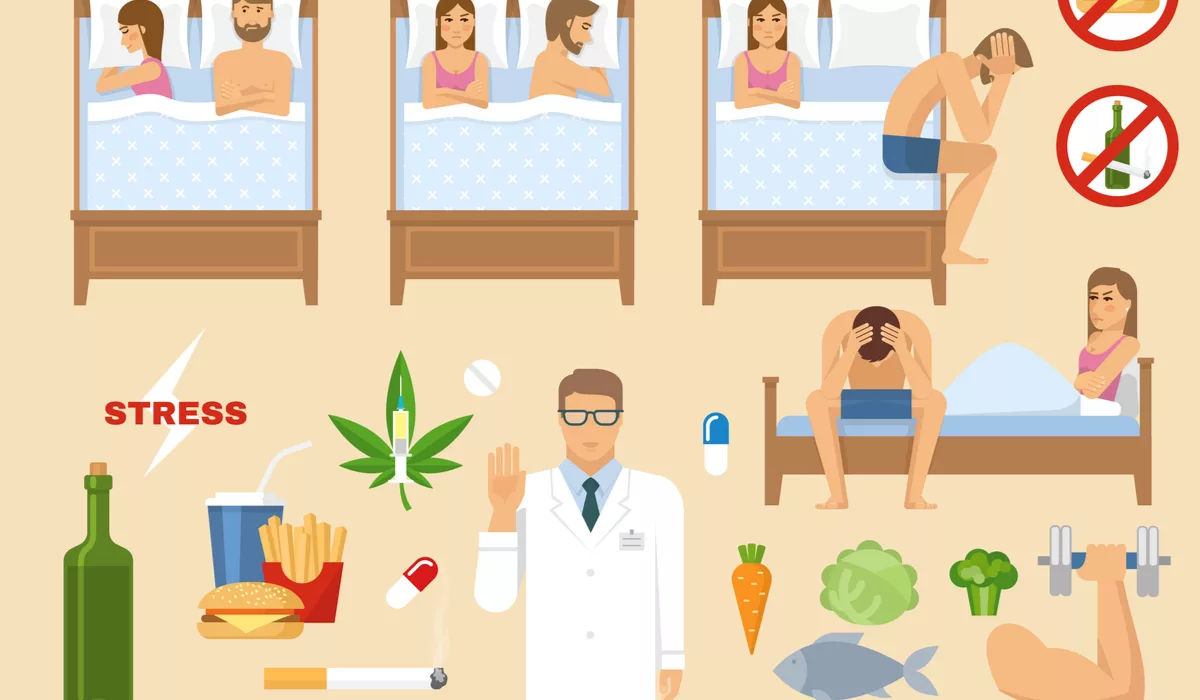

Lifestyle-related causes of erectile dysfunction (ED) are often associated with choices and habits that can contribute to the development or exacerbation of the condition. Lifestyle factors play a significant role in overall health, including sexual function.
Here are some common lifestyle-related causes of ED:
A. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking damages blood vessels, reducing blood flow throughout the body, including to the penis. It’s a significant risk factor for ED. Quitting smoking can improve both vascular health and sexual function.
B. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol use can impair sexual function, affecting both desire and the ability to maintain an erection. It’s essential to consume alcohol in moderation to minimize its impact on sexual health.
C. Obesity and Poor Diet
Obesity is linked to various health problems, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease, which can indirectly lead to ED. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help prevent and manage ED.
D. Lack of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining overall health, including sexual health. Exercise improves blood flow, helps control weight, and can positively influence hormonal balance, reducing the risk of ED.
E. Substance Abuse
The use of recreational drugs and substances can disrupt normal brain chemistry and contribute to ED. Seek help and support to overcome substance abuse issues and restore sexual function.
F. Sleep Deprivation
Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to fatigue, stress, and hormonal imbalances, all of which can contribute to ED. Prioritize healthy sleep habits to maintain optimal sexual health.
G. Bicycle Riding
Long periods of bicycle riding on a narrow, hard saddle can compress the perineal area and potentially cause nerve and blood vessel damage that leads to ED. Using a properly fitted saddle and taking breaks during rides can help mitigate this risk.
IV. Mixed Causes of Erectile Dysfunction

Erectile dysfunction (ED) is often the result of a combination of physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. These mixed causes can interact and compound one another, making it more challenging to pinpoint a single underlying cause.
Here are some scenarios where mixed causes of ED may be at play:
A. Age and ED
While aging itself is not a direct cause of ED, it is a risk factor. As men age, they are more likely to experience some of the physical and hormonal changes that can contribute to ED, such as decreased testosterone levels and vascular issues.
B. Combination of Factors
In many cases, ED is the result of a combination of physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. For example, a man with hypertension (physical) who experiences performance anxiety (psychological) may be at a higher risk. It’s essential to recognize and address all relevant factors when diagnosing and treating ED.
V. Prevention and Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction
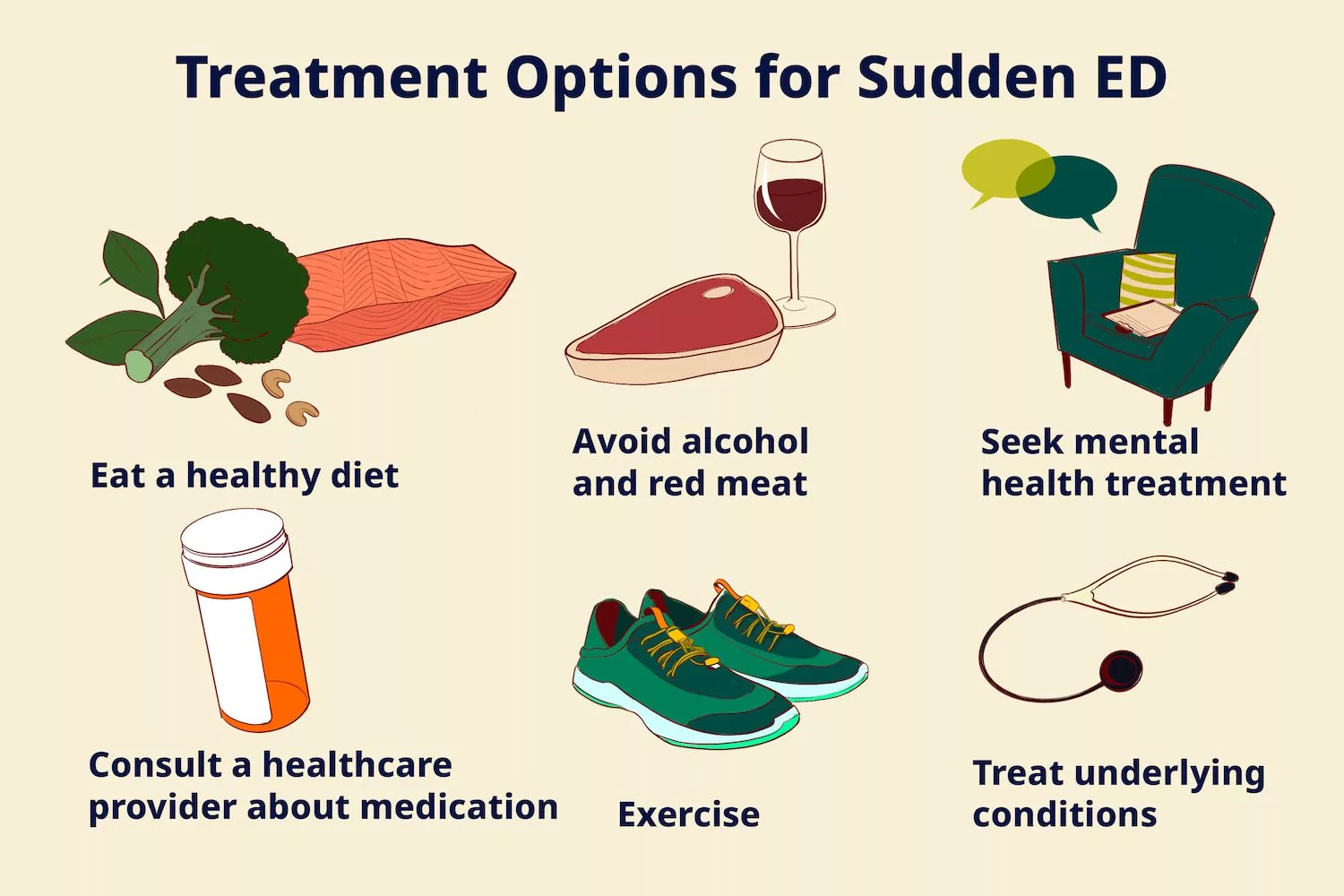
Preventing and treating erectile dysfunction (ED) involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both physical and psychological factors. Depending on the underlying causes, various strategies and treatments can be effective.
Make an Appointment Now!
Here’s a guide to prevention and treatment of ED:
A. Lifestyle Modifications
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major contributor to ED due to its negative impact on blood flow. Quitting smoking can lead to improved vascular health and increased sexual function.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Moderation is key when it comes to alcohol. Reducing excessive alcohol intake can help improve sexual performance.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can promote overall health and support sexual function.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve blood flow, maintain a healthy weight, and promote hormonal balance.
- Manage Stress: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and reduce its impact on sexual function.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritize good sleep hygiene to ensure you get sufficient rest and maintain optimal hormonal balance.
- Avoid Substance Abuse: Seek professional help and support if you are struggling with substance abuse issues.
B. Psychological Support
- Therapy: Individual or couples therapy can help address underlying psychological issues contributing to ED, such as anxiety, depression, or relationship problems.
- Sex Therapy: Sex therapists specialize in helping individuals and couples overcome sexual difficulties, including ED.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Techniques like mindfulness meditation and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce performance anxiety and stress.
C. Medications and Therapies
- Oral Medications: Medications like sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) are commonly prescribed to treat ED by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Hormone Therapy: In cases of hormonal imbalances, hormone replacement therapy may be considered to restore testosterone levels.
- Penile Injections: Some men may benefit from injecting medications directly into the penis to achieve and maintain an erection.
- Vacuum Erection Devices: These devices create a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into it and facilitating an erection.
- Penile Implants: Surgical implants can be an option for men who do not respond to other treatments. These devices can be inflated to create an erection.
D. Surgical Interventions
- Vascular Surgery: In cases where blood flow issues are the primary cause of ED, vascular surgery may be an option to improve blood circulation to the penis.
- Penile Implants: As mentioned earlier, penile implants involve surgically placing devices in the penis to facilitate erections.
E. Herbal Remedies and Supplements
While some herbal remedies and supplements are marketed as treatments for ED, their efficacy is not always well-established, and they should be used with caution. Consult with a healthcare provider before using any herbal or dietary supplements to address ED.
How Long Does Temporary Erectile Dysfunction Last?

Temporary erectile dysfunction, also known as situational or intermittent erectile dysfunction, can cause concern and uncertainty in men. Erectile dysfunction can be a distressing experience for men, raising questions about its duration and potential causes. The duration of temporary ED can vary depending on several factors, including the underlying cause, individual health, and psychological factors. Generally, temporary ED is short-lived and resolves spontaneously or with appropriate interventions. It is important to note that there is no fixed timeline, as the duration can differ from person to person. However, temporary erectile dysfunction typically lasts for a few days to a few weeks.
Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfucntion (ED)
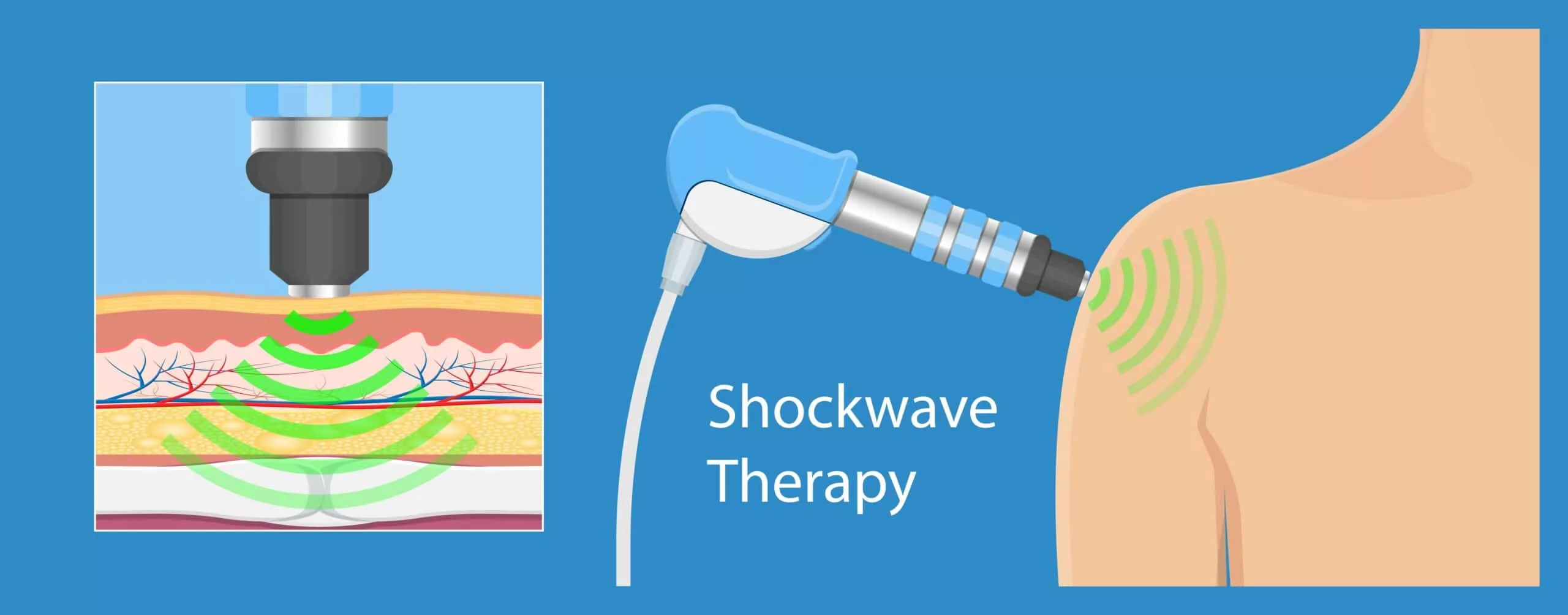
SWT for ED involves applying low-intensity shockwaves to the penis. The shockwaves stimulate the growth of new blood vessels and nerve tissue, which in turn improves blood flow to the penis and helps to increase the quality of erections. The treatment also helps to break down micro-plaque in the penile blood vessels, which can obstruct blood flow and contribute to ED. The shockwaves are delivered through a wand-like device that is placed on the penis. The treatment usually takes around 20 minutes, and patients typically require multiple sessions to achieve optimal results.
Conclusion: Causes for Erectile Dysfunction

Erectile dysfunction is a complex and multifaceted condition with a wide array of potential causes. Understanding these causes is the first step toward effective prevention and treatment. It’s crucial to recognize that ED is a common and treatable condition. If you or a loved one is experiencing ED, seeking help from a healthcare provider is the best course of action. By addressing the root causes, adopting a healthier lifestyle, and exploring available treatments, many men can regain their sexual confidence and overall well-being. Remember that you are not alone, and there is hope for a fulfilling and satisfying sex life.
Best Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) in Dallas, TX
What is the main cause of erectile dysfunction?
There are many neurological (nerve problems) causes of ED. Diabetes, chronic alcoholism, multiple sclerosis, heavy metal poisoning, spinal cord and nerve injuries, and nerve damage from pelvic operations can cause erectile dysfunction.
At what age do guys have trouble getting hard?
The most common sexual problem in men as they age is erectile dysfunction (ED). In general, the younger a man is, the better his sexual function will be. About 40% of men are affected by erectile dysfunction at age 40, and nearly 70% of men are affected by ED by the time they turn 70.
Can masturbation cause ED?
No, masturbation cannot cause ED - it is a myth. Masturbation is natural and does not affect the quality or frequency of erections. Research shows that masturbation is very common across all ages. Approximately 74 percent of males reported masturbating, compared to 48.1 percent of females.
How long can the average man stay erect?
Typically, an average erection may last from a few minutes to roughly half an hour. However, this can vary significantly due to the many factors that can affect erection duration. It is also worth noting that a person does not need an erection to achieve orgasm.
How can I fix ED naturally fast?
All people with ED are advised to try lifestyle modifications while they seek a formal diagnosis and treatment. For many people, lifestyle changes like eating a healthy diet, quitting smoking, exercising, limiting stress, avoiding alcohol, and talking to a therapist can cure ED without the use of medication.