Demystifying Erectile Dysfunction: A Comprehensive Guide
ED in Men | Can Masturbation Cause ED? | Shockwave Therapy for ED
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects millions of men worldwide. It is characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity. While it can be a sensitive topic for many individuals, understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for ED is essential in promoting overall sexual health and well-being. In this blog post, we will explore the various factors that contribute to erectile dysfunction, its associated symptoms, and the range of effective treatment options.
What is Erectile Dysfunction?

Erectile dysfunction, also known as impotence, refers to the consistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. It is important to note that occasional difficulties with erections are normal and do not necessarily indicate ED. However, if the problem persists for an extended period, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction

Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be caused by a variety of factors, including physical, psychological, and lifestyle-related issues. Understanding the underlying causes is essential in determining the appropriate treatment approach. Here are some common causes of erectile dysfunction:
Physical Factors Leading to Erectile Dysfunction
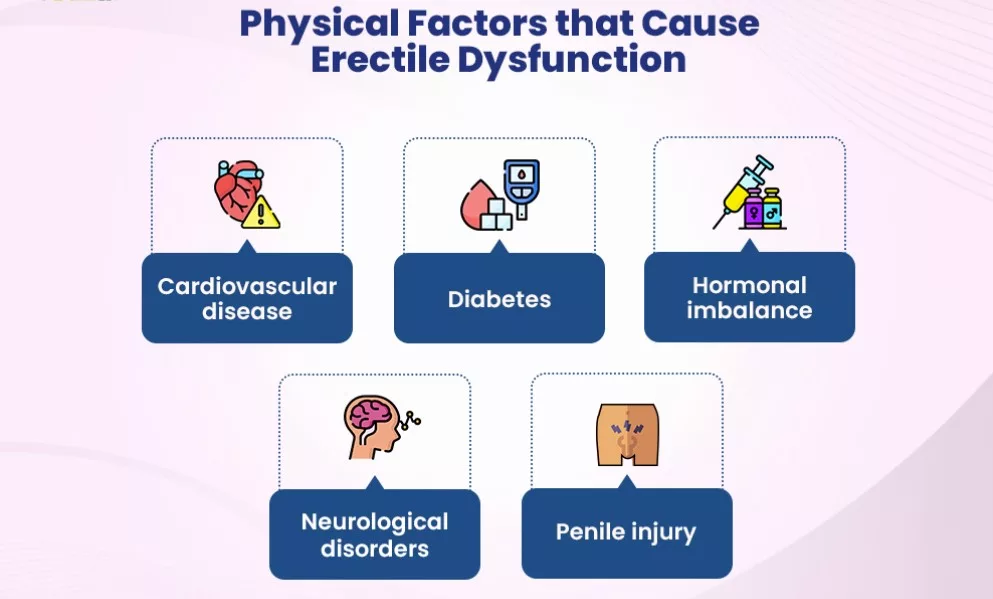
Physical factors play a significant role in the development of erectile dysfunction (ED). Here are some of the common physical causes:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Cardiovascular conditions that affect blood flow and blood vessel health can contribute to ED. Atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, can restrict blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection. High blood pressure (hypertension) and conditions like coronary artery disease also affect blood flow, potentially leading to ED.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal imbalances, particularly low testosterone levels, can contribute to erectile difficulties. Testosterone is a crucial hormone for male sexual health and plays a role in libido and the erection process. Reduced testosterone levels can result from conditions such as hypogonadism (low testosterone production) or hormonal disorders.
- Neurological Disorders: The nervous system plays a vital role in initiating and maintaining an erection. Neurological conditions that affect nerve function can interfere with the transmission of signals between the brain, spinal cord, and penis. Conditions like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and spinal cord injuries can disrupt these signals, leading to erectile problems.
- Medications and Substance Abuse: Certain medications can have side effects that impact erectile function. Antidepressants, antihistamines, blood pressure medications, and some prostate cancer treatments can cause or contribute to ED. Substance abuse, including alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drugs, can also affect sexual function by damaging blood vessels, reducing testosterone levels, or interfering with nerve function.
- Diabetes: Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that can damage blood vessels and nerves over time. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can affect the blood flow and nerve function necessary for achieving and maintaining an erection.
- Obesity: Obesity is linked to various health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and hormonal imbalances. Excess body weight can affect hormone levels, blood flow, and overall cardiovascular health, contributing to ED.
- Pelvic Surgeries or Injuries: Surgeries or injuries that affect the pelvic region, such as prostate surgery, bladder surgery, or pelvic fractures, can damage nerves, blood vessels, or tissues involved in the erection process. This damage can result in temporary or permanent erectile difficulties.
- Other Medical Conditions: Several other medical conditions can contribute to ED. These include kidney disease, liver disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and certain cancers.
Make an Appointment Now!
It’s important to note that individual cases of ED may involve a combination of physical factors. Identifying the underlying cause is essential for determining the appropriate treatment approach. If experiencing erectile difficulties, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to explore the physical factors and develop an effective treatment plan.
Psychological Causes of Erectile Dysfunction

Psychological factors can significantly contribute to the development or worsening of erectile dysfunction (ED). Here are some common psychological causes:
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can interfere with the physiological processes necessary for achieving and maintaining an erection. Stress related to work, finances, relationships, or performance can create a mental and emotional burden that impacts sexual function.
- Performance Anxiety: Fear of not being able to perform sexually or satisfy a partner can create performance anxiety. This anxiety can lead to a self-perpetuating cycle of worry and stress, making it difficult to achieve or sustain an erection.
- Depression: Depression is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities. These feelings can extend to sexual experiences, resulting in decreased libido and difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Relationship Issues: Relationship conflicts, communication problems, unresolved emotional issues, or a lack of intimacy can contribute to ED. The emotional strain and tension within a relationship can negatively impact sexual desire and function.
- Body Image Issues: Negative body image and low self-esteem can significantly affect sexual confidence and performance. Feeling insecure about one’s appearance or physical attributes can create anxiety and self-doubt during sexual encounters, leading to difficulties with erections.
- Sexual Trauma or Abuse: Past experiences of sexual trauma or abuse can have a lasting impact on sexual function. The psychological effects of trauma can manifest as ED or other sexual disorders.
- Unrealistic Expectations: Unrealistic expectations about sexual performance or body image, often influenced by societal or media standards, can create pressure and anxiety. These expectations may lead to feelings of inadequacy and difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Psychological Disorders: Certain psychological disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and performance anxiety disorder, can contribute to ED. These disorders are characterized by excessive worry, fear, or intrusive thoughts that can affect sexual functioning.
It is important to note that psychological factors can often coexist with physical causes of ED, and they may interact and influence each other. Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor experienced in sexual issues can be beneficial in addressing and managing the psychological aspects of erectile dysfunction. Combining psychological interventions with medical treatments can lead to improved sexual function and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Factors contributing to ED
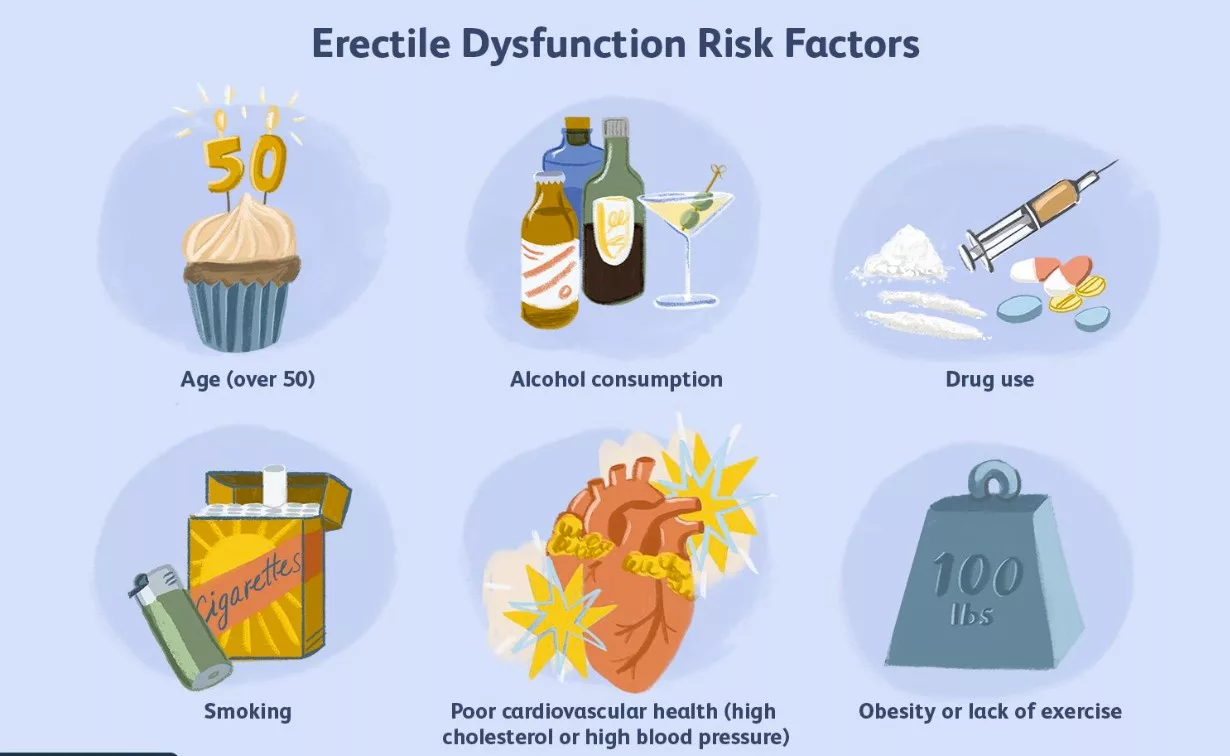
Lifestyle factors can significantly contribute to the development or worsening of erectile dysfunction (ED). Making positive changes in these areas can help improve erectile function. Here are some common lifestyle factors that can lead to ED:
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for ED. Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces blood flow throughout the body, including the arteries that supply the penis. This restriction of blood flow can make it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to obesity, cardiovascular problems, and reduced blood flow, all of which can impact erectile function. Regular exercise helps improve cardiovascular health, promotes blood flow, and enhances overall sexual function.
- Poor Diet: A diet high in processed foods, saturated fats, and refined sugars can lead to obesity, diabetes, and other conditions that increase the risk of ED. Eating a healthy and balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can reduce the risk of ED by supporting overall cardiovascular health and blood vessel function.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: While moderate alcohol consumption may not have a significant impact on erectile function, excessive drinking can lead to ED. Alcohol is a depressant that can affect sexual desire, impair nerve function, and cause hormonal imbalances, all of which can contribute to difficulties with erections.
- Illicit Drug Use: Illicit drug use, such as cocaine, marijuana, and opioids, can have detrimental effects on sexual function. These substances can disrupt hormone levels, impair nerve function, and interfere with the blood flow necessary for achieving and maintaining an erection.
- Obesity: Obesity is a known risk factor for ED. Excess body weight can lead to hormonal imbalances, such as low testosterone levels, and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Both of these factors can contribute to erectile difficulties.
- Stress and Mental Health: Chronic stress, anxiety, and mental health conditions can negatively impact sexual function. High-stress levels can increase cortisol levels, which can interfere with hormone production and affect sexual desire and performance. Prioritizing stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises, meditation, or therapy, can help improve overall sexual health.
- Medications and Substance Abuse: Certain medications, including antidepressants, antihistamines, and blood pressure medications, can have side effects that affect erectile function. Substance abuse, including alcohol and illicit drug use, can also impair sexual function and contribute to ED.
Call to Book your FREE Consultation
By adopting a healthier lifestyle and making positive changes, individuals can reduce the risk of developing ED or improve their existing condition. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance in managing lifestyle factors and improving erectile function.
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction
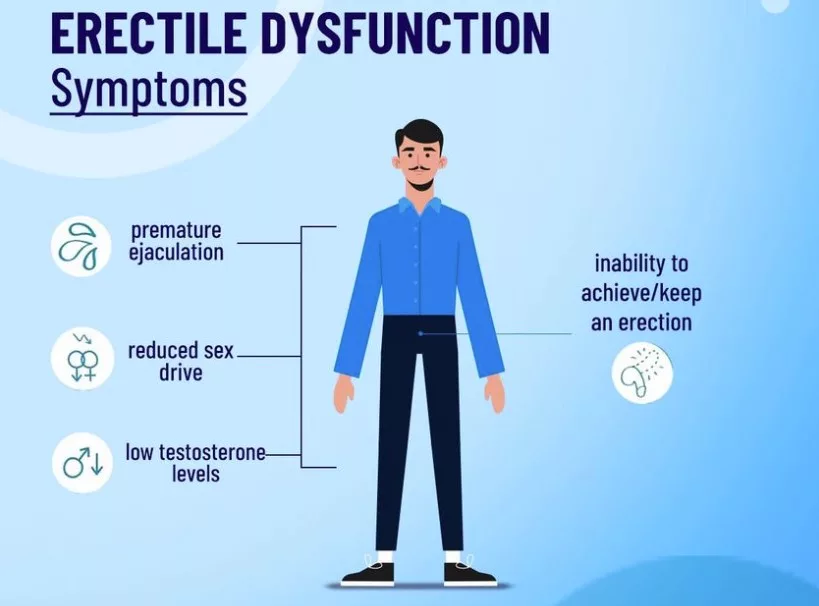
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is characterized by the consistent or recurrent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. The primary symptom of ED is the difficulty in getting or keeping an erection. However, there are other associated symptoms and signs that may indicate the presence of erectile dysfunction. Here are some common symptoms:
- Difficulty Achieving an Erection: The inability to achieve an erection is one of the main symptoms of ED. Men with ED may find it challenging to get an erection even when sexually stimulated.
- Difficulty Maintaining an Erection: Another symptom of ED is the inability to sustain an erection throughout sexual activity. Men may experience the loss of erection before or during intercourse, making it difficult to engage in satisfactory sexual intercourse.
- Reduced Sexual Desire: While ED primarily affects the physical aspect of achieving and maintaining an erection, it can also impact sexual desire or libido. Men with ED may experience a decrease in their interest or desire for sexual activity.
- Premature or Delayed Ejaculation: In some cases, ED can be associated with ejaculatory disorders. Men with ED may experience premature ejaculation, where ejaculation occurs too quickly, or delayed ejaculation, where it takes an extended period to ejaculate despite adequate sexual stimulation.
- Emotional Distress or Psychological Impact: ED can lead to emotional distress, including feelings of frustration, embarrassment, low self-esteem, or anxiety related to sexual performance. The impact of ED on a man’s psychological well-being and relationships can be significant.
It’s important to note that occasional difficulties with erection do not necessarily indicate ED. ED is diagnosed when the symptoms persist over a consistent period, typically for several months. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in sexual health. They can conduct a thorough evaluation, review medical history, and perform any necessary tests to determine the cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Remember, open communication and seeking help are crucial steps in addressing and managing erectile dysfunction effectively.
Available Treatments for Erectile Dysfunction

There are several effective treatments available for erectile dysfunction (ED) that can help men regain and maintain satisfactory erectile function. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause of ED, individual preferences, and overall health. Here are some common treatments for ED:
- Oral Medications (Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors): Medications such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), and avanafil (Stendra) are commonly prescribed for ED. These drugs work by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating the ability to achieve and maintain an erection in response to sexual stimulation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making certain lifestyle changes can improve erectile function. These may include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and managing stress. Lifestyle modifications can have a positive impact on overall cardiovascular health and blood flow, thereby improving erectile function.
- Psychological Counseling: If psychological factors, such as anxiety, stress, or relationship issues, contribute to ED, psychological counseling or therapy may be beneficial. Counseling can help address underlying emotional issues, enhance communication, reduce performance anxiety, and improve overall sexual well-being.
- Vacuum Erection Devices (VEDs): A vacuum erection device is a non-invasive device that creates a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into the organ and facilitating an erection. Once the erection is achieved, a constriction ring is placed at the base of the penis to maintain the erection. VEDs can be an effective treatment option, especially for men who cannot or do not want to use medication.
- Penile Injections: Injecting medication directly into the base or side of the penis can help achieve an erection. The most commonly used medication for penile injections is alprostadil, which dilates blood vessels and increases blood flow. This treatment is effective for many men, but it requires proper training for self-injection.
- Penile Implants: In more severe cases of ED that do not respond to other treatments, surgical options like penile implants may be considered. Penile implants are devices surgically inserted into the penis to provide an erection when desired. They can be inflatable or malleable, allowing for an erection on demand.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): If low testosterone levels contribute to ED, testosterone replacement therapy may be recommended. TRT involves administering testosterone through injections, patches, gels, or pellets to restore testosterone levels to a normal range. However, TRT is not suitable for all men, and its use requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional specializing in sexual health to determine the most appropriate treatment for ED. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors, and a comprehensive evaluation will help identify the underlying cause and tailor the treatment plan accordingly.
Conclusion: Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction is a prevalent condition that can significantly impact a man’s well-being. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, individuals can take the necessary steps to address this issue. Seeking medical advice is essential to diagnose the underlying cause accurately and develop an effective treatment plan. Remember, ED is a treatable condition, and with the right support, many men can regain their sexual health and overall quality of life.
Find Best Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction in Dallas, TX

Call Us Today
+1-888-816-9362
Moreover, we have created a setting where you can seek treatment for erectile dysfunction without fear or shame because we recognize the physical and emotional sensitivity of the condition.
Make an Appointment Now!
Can masturbation cause ED?
No, masturbation cannot cause ED – it’s a myth. Masturbation is natural and does not affect the quality or frequency of erections. Research shows that masturbation is very common across all ages. Approximately 74 percent of males reported masturbating, compared to 48.1 percent of females.
How do guys feel when they can't get it up?
A man with ED may emotionally feel arousal, but the penis may be unable to maintain an erection. This may lead to frustration, feelings of inadequacy, emasculation, and shame. A person may fear being unable to fulfill the sexual needs of their partner.
How long can the average man stay erect?
A penile erection can normally last anywhere from a few minutes to about half an hour. On average, men have five erections a night while they’re sleeping, each lasting about 25 to 35 minutes.
Can lack of sperm cause ED?
However, some medical conditions that cause low sperm count may also cause ED. A 2020 study found that newly-married men with ED were also more likely to have low sperm counts. This may be because of common risk factors and medical conditions that can cause each health issue.
Can a man with erectile dysfunction satisfy a woman?
Even if you can’t maintain a firm erection, you may still be able to orgasm. Even without intercourse, you and your partner can give each other a great deal of sexual pleasure.